Manual Removal Of Placenta Complications
3 23 continued bleeding after cesarean section to evaluate for retained products of conception suture or a cesarean section pouch in the lower uterine segment.
Manual removal of placenta complications. Although it increases the likelihood of bacterial contamination in the uterine cavity there are no randomised controlled trials to evaluate the effectiveness of antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent endometritis after manual removal of placenta. The complications may occur as a consequence of manual removal of retained placenta. Manual removal of the placenta after delivery with continued postpartum bleeding to evaluate for retained placenta fragments fig.
There is the threat of possible infection. Our aim is to provide expected outcomes for undergoing manual removal of placenta mrop following vaginal delivery in women having an unpredictable adherent placenta ap. An historical prospective study of all parturients undergoing manual placental removal between 2012 and 2014.
Manual removal of a retained placenta is not without risk. Delay of placental birth may cause severe fatal hemorrhaging. Sometimes the prophylactic usage of antibiotics may prevent the later infection.
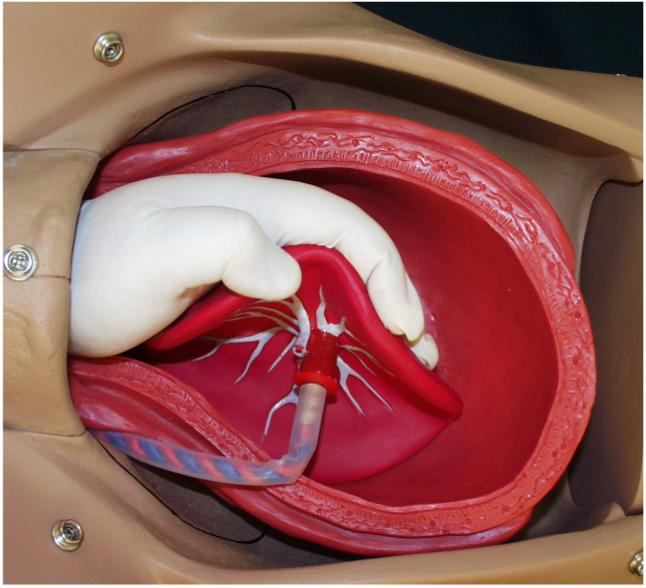
Provide emotional support and encouragement. Removal of the placenta from the womb is the only treatment option for a retained placenta however there are different methods of manual removal. Essential drugs for managing complications in pregnancy and childbirth manual removal of placenta review for indications.
During the manual removal genital tract can be damaged and bacteria can be introduced so that a woman may eventually end up with severe puerperal infection. Parturients were matched by time of delivery with parturients delivering vaginally with spontaneous placental separation. Manual placenta removal is an emergency procedure.
You can opt for an anesthetic and the ob gyn can try to remove it manually but the risk of infection is elevated. Despite scant evidence it is commonly advised that if the placenta has not been expelled 30 minutes after delivery manual removal of the placenta should be carried out under anaesthesia. Review general care principles and start an iv infusion.
Therefore a pre or intrapartum screening opportunity for placenta accreta would be desirable. Complications indicating manual placenta removal arise when the placenta fails to descend into the birth canal.